
Cloud Engineer, from Ostermundigen
#knowledgesharing #level 300
Near Real Time Data Ingestion into SageMaker Feature Store
The objective
This blog post is the first part of a 3 parts series about testing a fully automated MLOps pipeline for machine learning prediction on near real time timeseries data in AWS. This part focuses on the data ingestion pipeline into Amazon SageMaker Feature Store.
The entire demo code is publicly available in the project repository on GitHub.
Sagemaker Feature Store
For this demo, we have chosen to use the Amazon SageMaker Feature Store as the final repository of the data ingestion pipeline. As per the documentation:
“Amazon SageMaker Feature Store is a fully managed, purpose-built repository to store, share, and manage features for machine learning (ML) models.
Features are inputs to ML models used during training and inference.”
The Demo
The demo ingests blockchain transactions from the blockchain.com API (see documentation here). Based on the data it ingests, the pipeline computes and stores 3 simple metrics in Amazon SageMaker Feature Store:
- The total number of transactions
- The total amount of transaction fees
- The average amount of transaction fees
These metrics are computed per minute. Although it might not be the best window period to analyze blockchain transactions, it allows us to quickly gather a lot of data points in a short period of time, avoiding running the demo for too long which has an impact on the AWS costs.
This demo is developed using the AWS CDK and is available here.
The Architecture
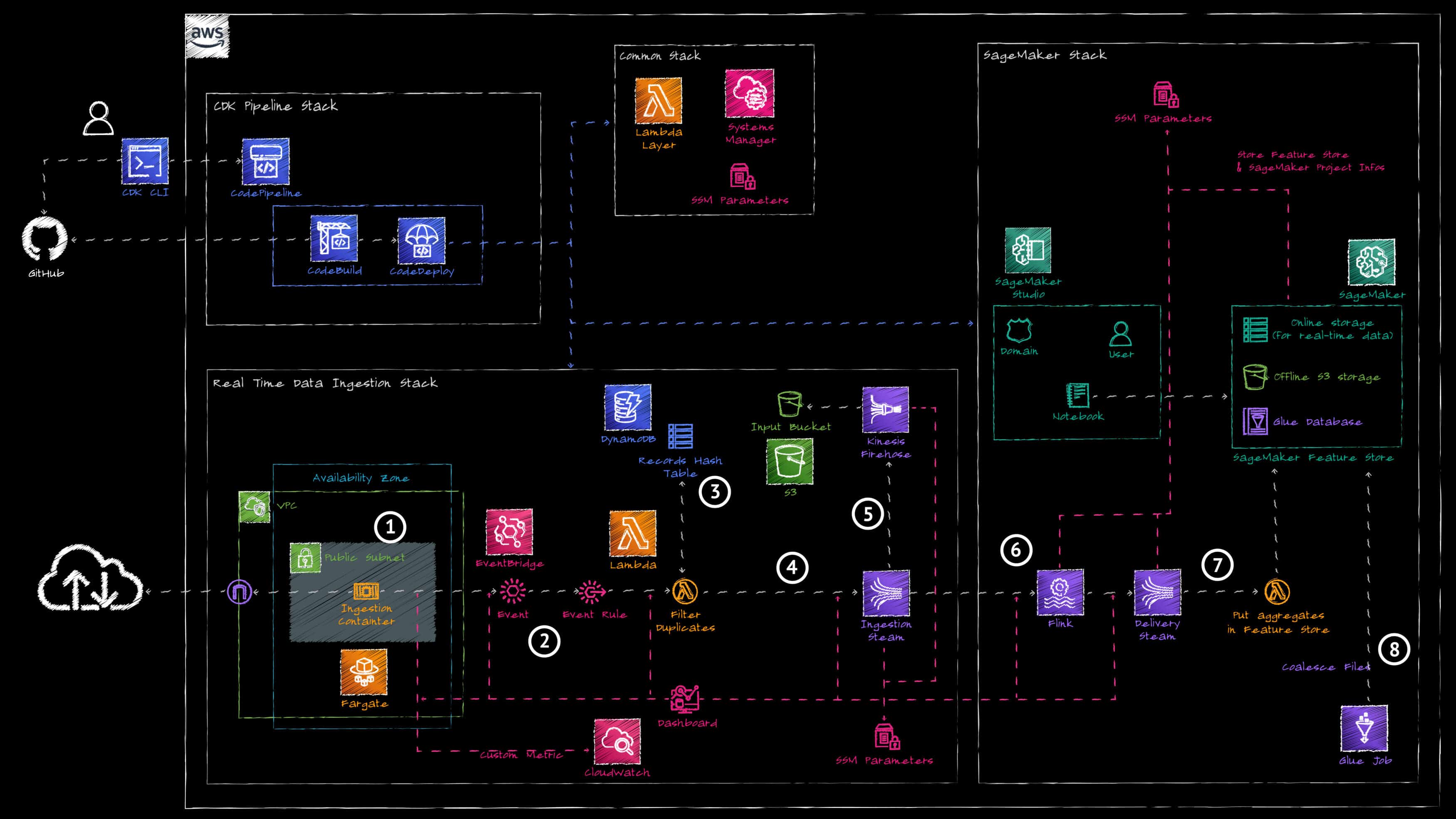
The project is made of a self-mutating pipeline which deploys the different stacks of the project. Only the data ingestion pipeline components are shown here (the MLOps part of the architecture will be detailed in future posts).
The pipeline works as follow:
1. An AWS Fargate container polls the data source API every 15 seconds to ingest the last 100 transactions and publish all transactions on the data ingestion event bus of AWS EventBridge.
2. An AWS EventBridge Rule routes the ingested data to an AWS Lambda Function.
3. The AWS Lambda Function is used in combination with Amazon DynamoDB to keep track of recently ingested transactions and filter out transactions already ingested.
4. The filtered data are written into an Amazon Kinesis Data Stream.
5. The ingestion data stream is connected to an Amazon Kinesis Firehose stream which stores the raw data to an Amazon S3 Bucket for archival.
6. An Amazon Managed Service for Apache Flink application reads the data from the ingestion stream and uses a tumbling window to compute the following 3 metrics per minute:
a. total number of transactions
b. total amount of transaction fees
c. average amount of transaction fees
7. The Flink application writes the aggregated data to a delivery Amazon Kinesis Data Stream. An AWS Lambda Function reads from the delivery stream and writes the aggregated data to Amazon SageMaker Feature Store.
8. An AWS Glue Job periodically aggregates the small files in the Amazon SageMaker Feature Store S3 Bucket to improve performance when reading data.
In addition to deploying the data ingestion pipeline, the infrastructure stack also deploys the data scientist environment using Amazon SageMaker Studio. It creates an Amazon SageMaker Studio Domain and creates a user in it with the appropriate permissions. With this, the data scientist has access to an IDE to run Jupyter Notebooks to perform analytics on the data, run experiments and test training a model.
How to look at the data being ingested?
Monitoring the Pipeline
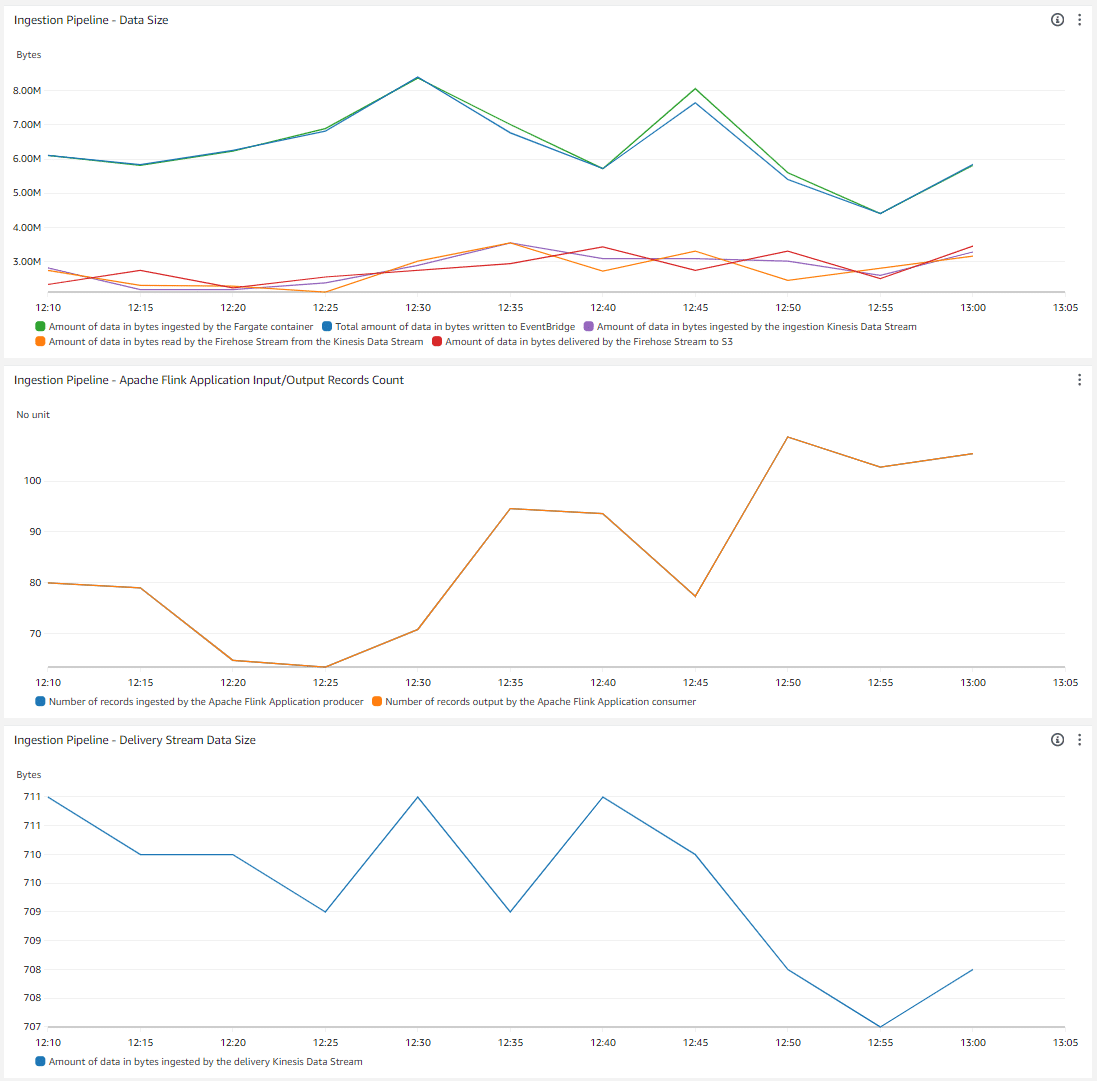
The demo comes with a CloudWatch dashboard for you to see the data flowing through the different components. It displays in the first widget the amount of bytes:
- Ingested by the AWS Fargate Container
- Ingested by AWS EventBridge (There is unfortunately no metric per AWS EventBridge bus. This metric shows the total amount of data ingested by EventBridge in the account)
- Ingested by the Amazon Kinesis Data Stream ingestion stream
- Ingested by Amazon Kinesis Firehose from the ingestion stream
- Delivered by Amazon Kinesis Firehose to Amazon S3
The second widget displays the number of records output by the Apache Flink Application consumer and ingested by the Apache Flink Application producer (should be equal when the Flink application works correctly). The third widget shows the amount of bytes ingested by the Amazon Kinesis Data Stream delivery stream (1 record per minute).
Querying the Data using Amazon Athena
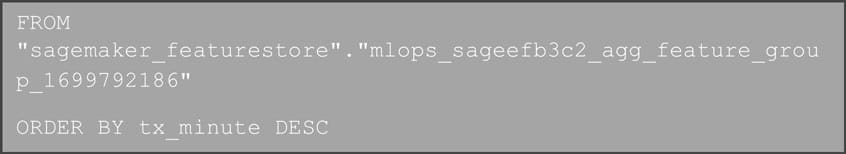
Querying the Data using Amazon SageMaker Studio Notebook
In the repository /resources/sagemaker/tests/ folder we provide a Jupyter notebook read_feature_store.ipynb to read the latest entry in the online store. From the Amazon SageMaker Studio domain, you can use the provisioned user and launch a studio application. Once in the Jupyter or Code Editor environment, you can upload that notebook and run it. The notebook reads the latest data point from the Online Store of Amazon SageMaker Feature Store.
You will observe a roughly 6 minutes difference between the timestamp of the latest data available in the Online Store versus the Offline Store of Amazon SageMaker Feature Store.
The Challenges
The main challenge we faced when developing this architecture with the CDK was the cleanup of the SageMaker domain. When creating a SageMaker domain, AWS creates an Amazon EFS share with endpoints in the VPC and NSGs attached to them. When a user starts a SageMaker Studio App, compute resources are deployed to host the Code Editor/Jupyter IDE session and Jupyter kernel session. None of those resources are deleted automatically when deleting the domain. This means that a Custom Resource must be developed in the CDK Stack to clean up the domain before it gets deleted. The main issue is that deleting a SageMaker Studio App can take more than the 15 minutes maximum runtime of the Custom Resource Lambda Function. Implementing a Step Function to periodically check the SageMaker Studio App status and wait for the deletion does not help because Cloud Formation WaitCondition does not support deletes and thus does no wait to receive the signal back from the Custom Resource before continuing with deletion.
Two issues have been opened in the CloudFormation repository:



